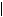 Ψi(x, y, z)
Ψi(x, y, z)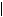 2 for the given state i in the point (x, y, z) gives the probability of the electron location in the volume dxdydz: pi(x, y, z) =
2 for the given state i in the point (x, y, z) gives the probability of the electron location in the volume dxdydz: pi(x, y, z) = 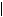 Ψi(x, y, z)
Ψi(x, y, z)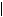 2dxdydz.
2dxdydz.
WAVE FUNCTION
According to the quantum-mechanical theory, position of an electron in space is described by the wave function Ψ(x, y, z), which depends on the space coordinates x, y, z. The wave function is a complex value. It is also called psi-function. The square of the absolute value of the wave function 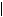 Ψi(x, y, z)
Ψi(x, y, z)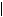 2 for the given state i in the point (x, y, z) gives the probability of the electron location in the volume dxdydz: pi(x, y, z) =
2 for the given state i in the point (x, y, z) gives the probability of the electron location in the volume dxdydz: pi(x, y, z) = 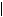 Ψi(x, y, z)
Ψi(x, y, z)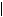 2dxdydz.
2dxdydz.
States, in which the energy of particle E has definite values, are called steady states. Such states are described by wave functions of steady states ψn. For wave functions of steady states Schroedinger's equation for steady states is fair:
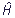 ψn = Eψn.
ψn = Eψn.
E here is the energy of the particle: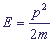 , where p is the impulse of the particle, and m is its mass.
, where p is the impulse of the particle, and m is its mass.
Arbitrary wave function can be expanded by wave functions of steady states:
 .
.
For an arbitrary wave function Schroedinger's equation has the form:
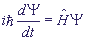 .
.
 is the Hamiltonian of a free-moving particle.
is the Hamiltonian of a free-moving particle.