Russian
MASS ACTION LAW
The essence of the mass action law (the law of mass action) is in the fact, that the rate of an elementary chemical reaction is proportional to the
concentration of the reacting substances in the degrees, which are equal to stoichiometric coefficients of these substances in the chemical equation. For a reaction
nAA + nBB + ... → nCC + nDD + ...
the mass action law is written in the following way:
v = 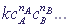 , where
, where
cA, cB, ... - are concentrations of reacting substances A, B, ... ;
nA, nB, ... - are the degrees of order of the reaction to the corresponding agents (as a rule, they coincide with the stoichiometric coefficients of these reagents in the chemical equation);
k is the coefficient of proportionality, the constant of the reaction rate, which depends on the nature of the reacting substances and on the
temperature;
v - is the reaction rate.
The title of the given equation is kinetic chemical equation.
In the state of thermodynamic equilibrium the concentrations of all the reacting substances are associated, according to the mass action law, by the ratio (
equilibrium constant):
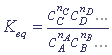
The concentration of the solid substance in the process of chemical transformation does not change (the process goes on the surface), that is why the rate in reactions, where solid substances participate, is determined only by the concentration of gases or dissolved substances.
In complex (multistage) reactions the rate of the whole process depends on the rate of the most slow reaction.
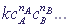 , where
, where