RNA

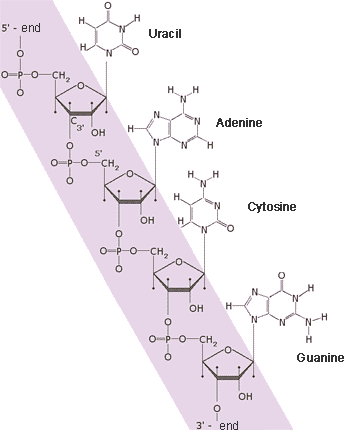
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a biological
polymer, similar to DNA in its chemical structure. An RNA molecule consists of the same
monomer links as
DNA,
nucleotides. The differences concern, firstly, sugar in the structure of the nucleotides; secondly, in the structure of RNA uracil nucleotide presents instead of thymine nucleotide in DNA. In the nature RNA exists, as a rule, as a single chain. In some viruses RNA contains the genetic information. In a cell RNA plays an important role in transfer of information from DNA to proteins. RNA is synthesized on a DNA-matrix. This process is called
transcription. DNA has sections, where the information responsible for synthesis of three kinds of RNA is contained. The three kinds of RNA differ in the functions they perform: messenger RNA (
mRNA), ribosomal RNA (
rRNA), and transfer RNA (
tRNA). All the three kinds of RNA participate in protein
synthesis in one or another way. However, the information on the
protein synthesis is contained only in mRNA.
|
Supplementary information
|