NUCLEOTIDES

Nucleotide is the main repeating unit in molecules of
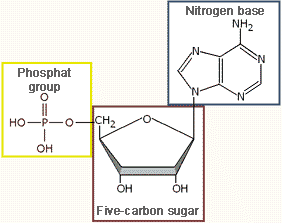
nucleic acids. Nucleotide is the product of chemical bonding of a nitrogen base, a five-carbon sugar (a pentose), and one or several phosphate groups. Nucleotides in the nucleic acids contain one phosphate group. They are names according to the nitrogen base which they contain: adenine nucleotide (A), if it contains adenine, guanine nucleotide (G), - if guanine, cytosine nucleotide (C), - if cytosine, thymine nucleotide (T) - if thymine, uracil nucleotide (U) - if uracil. Constituents of a
DNA are 4 types of nucleotides: A, T, G, C. Constituents of an
RNA are also 4 types: A, U, G, C. The sugar in the structure of all DNA nucleotides is deoxyribose, in RNA nucleotides it is ribose. While forming nucleic acids, nucleotides bond with each other and make
sugar-and-phosphate core, and the bases are on one side of it.
|
Supplementary information
|