Russian
ION-DIPOLE INTERACTIONS
Ion-dipole interactions belong to weak, nonvalent bonds. They are of non-chemical nature. They are interactions between ions and polar groups of molecules. Ion-dipole interactions play the important role in mane biological systems.
The potential attraction energy between an ion and a static constant dipole is inversely proportional to the squared distance between them:
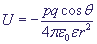 , where
, where
p - is the dipole moment of the static dipole,
q - is the ion charge,
θ - is the angle between the field vector and the dipolar moment,
ε - is the electric permittivity of medium,
ε0 - is the electric permittivity of vacuum,
r - is the distance between the ion and the dipole.
The potential attraction energy between an ion and a movable constant dipole is inversely proportional to the biquadratic distance between them:
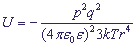 ,where
,where
k - is the Boltzmann constant,
T - is the absolute temperature .
The attraction energy between an ion and an induced dipole is inversely proportional to the biquadratic distance, that is why it decreases much faster while the distance is decreasing:
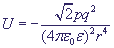 .
.
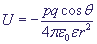 , where
, where
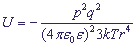 ,where
,where
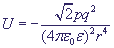 .
.