Keq =
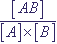 , where
, where 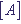 ,
, 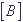 ,
, 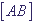 are concentrations of atoms of types A, B and AB in mole/l correspondingly.
are concentrations of atoms of types A, B and AB in mole/l correspondingly.
EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
Chemical equilibrium constant is the value, which expresses interdependence between concentrations of substances in a system when chemical equilibrium is obtained. Numerical values of chemical equilibrium constants allow calculating of yield of a product of a chemical reaction in given conditions on concentrations of the interacting substances.
Every
chemical bond is the result of activity of two opposite forces, that is, the forces, which form the bond (electrostatic interaction), and the forces, which destroy it. Coupling reaction between two atoms A and B is described by the expression
A + B → AB + energy,
where AB is the obtained compound.
Bond formation is always accompanied by releasing of a certain amount of internal energy of atoms and its transfer into another form of energy.
Reaction rate is proportional to frequency of collisions between atoms A and B. When equilibrium is obtained, in a bounded system at any instant the number of newly formed bonds is exactly equal to the number of broken bonds. According to the
mass action law, the process is described by the expression for the equilibrium constant Keq:
Keq = 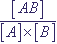 , where
, where  ,
, 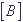 ,
, 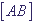 are concentrations of atoms of types A, B and AB in mole/l correspondingly.
are concentrations of atoms of types A, B and AB in mole/l correspondingly.